What is MCP and Why It’s the Future of AI Integration
The buzz around "MCP servers" is everywhere; it's the next big thing in AI integration. With MCP, AI can do more than just answer questions—it’s like a bridge that connects AI models to the outside world, enabling them to access external data, tools, and resources for more informed and dynamic responses.
In this article, we’ll simplify the concept of MCP, explore its real-world applications, and highlight how it stands apart from traditional AI models.
By the end, you'll have a clear understanding of what MCP servers are, why they’re so crucial, and how they’re reshaping the future of AI integration.
Start using 1,500+ MCP Servers for free and seamlessly connect to AI with just a URL.
Get Started for FreeTable of Contents :
What is MCP?
LLM Models Before MCP
LLM Models After MCP
How does MCP work?
Real-World Examples of MCP Servers in Action
Current Status of MCP Servers
Welcome to the Age of AI That Connects to Everything
What is MCP?
MCP (Model Context Protocol) is an open standard that allows AI models to interact with external applications in a simple and standardized way, enabling more complex and dynamic interactions. Confused? 🤔
Let’s think of it like your phone: Just as you add apps to your phone to expand its functionality, MCP is like adding apps, but for AI. Just as apps enhance what your phone can do, MCP extends the capabilities of AI by connecting it to external data and tools.
This allows AI to do more than just answer questions—it can access the latest information and interact with the world around it, just like your phone does with its apps.
You (or the AI) no longer need to manually switch contexts or learn each tool’s API; the MCP “translator” bridges the gap between human language and software commands.
In a nutshell, MCP is like giving your AI assistant a universal remote control to operate all your digital devices and services. Instead of being stuck in its own world, your AI can now reach out and press the buttons of other applications safely and intelligently. This common protocol means one AI can integrate with thousands of tools as long as those tools have an MCP interface – eliminating the need for custom integrations for each new app. The result: your AI helper becomes far more capable, able to not just chat about things but take actions in the real software you use.
LLM Models Before MCP
LLMs (Large Language Models) are advanced prediction models that are powerful in generating text and image-based responses based on general user queries.
But they face several key limitations, let's discussed it one by one:
1.Static Data and Lack of Real-Time Access in AI Models
AI models have very limited context and cannot access the latest information.Their responses are constrained to the information available in their training set, meaning they can only answer questions based on what they "know."
This can lead to static and sometimes outdated responses, as AI models cannot reach beyond their dataset to gather new insights or interact with the real world. For instance, GPT-4’s knowledge cuts off in April 2023, so it cannot provide information or updates beyond that date.
For example, if you asked a 2020-era model to check the weather or update a spreadsheet, it couldn't do it. Its capabilities were limited to producing text, with no access to live data or external tools.
2.Lack of Standard Protocol for AI-Tool Interaction
Traditionally, connecting an AI system to external tools involves integrating multiple APIs, each with its own unique set of requirements. Each API connection requires developers to write separate code, handle its specific authentication methods, document its usage, and implement error handling and maintenance processes.
This creates a complex and fragmented system where each API acts like an individual door, with its own key and set of rules to follow.
In this traditional approach, developers had to manually connect each tool to the AI, often using different approaches for each one. For instance, one tool might require the AI to output JSON, while another needed a custom Python wrapper or a specific prompt format. There was no unified standard for the AI to recognize available tools or how to use them; everything was hard-coded and bespoke. This made integration cumbersome and time-consuming.
3.One-Way Communication in AI Models
Currently, AI models primarily function in a one-way communication model, where they receive information or data from external sources but do not have the capability to trigger actions or send information back to external systems.
This creates a limitation in fully integrating AI into dynamic, real-time environments where reciprocal communication is essential.
As a result, the flow of information remains unidirectional, reducing the potential for real-time responses, adaptive decision-making, and interactive automation across systems.
4.Language Barrier in Tool Integration
A major obstacle in tool integration was the "language mismatch" between different software and services. Each platform had its own API, data format, and terminology, meaning an AI agent had to understand the specific nuances of each one.
For example, fetching a Salesforce report, querying a SQL database, or editing a Photoshop file are entirely different tasks with their own unique procedures. In a pre-MCP world, this mismatch required the AI's "intent" to be translated into each tool's specific dialect—often through complex prompt engineering or custom code.
LLM Models After MCP
“even the most sophisticated models are constrained by their isolation from data - trapped behind information silos…Every new data source requires its own custom implementation, making truly connected systems difficult to scale.”
MCP addresses this fragmentation head-on by offering one common protocol for all these interactions.
1.Improving AI Responses with Real-Time Context
With MCP, AI models gain access to real-time data and specialized tools, significantly enhancing their understanding of the context in which they're operating. This means that, instead of relying solely on pre-existing training data, the AI can pull in current, up-to-date information that is directly relevant to the situation at hand.
For example, a virtual assistant using MCP can track your food preferences shared on Slack. If you recently mentioned a dislike for spicy food, it can instantly adjust its recommendations, suggesting milder options, rather than relying on outdated, generic suggestions. This allows for real-time, personalized responses based on the most current information.
This way, the AI can offer timely, context-aware responses instead of offering outdated or irrelevant information.
2.MCP Becomes the Standard Protocol for AI-Tool Interaction
MCP is the HTTP of AI. MCP is doing for AI what HTTP did for the web. It enables AI to integrate with everything:
- Universal Communication Standard
- Reduces Complexity in AI systems
- Enables seamless data exchange.
HTTP standardized the way websites communicate and interact with each other, creating a universal protocol that enabled the web to flourish.
Similarly, MCP is set to standardize AI agents, providing a unified protocol that allows different AI models and systems to seamlessly communicate and collaborate with one another.
Just as HTTP brought order and structure to web communication, MCP will establish a consistent framework for AI agents to interact across various platforms and tools. It will become the single key that unlocks all the doors for AI models, enabling seamless communication and integration across diverse systems.
This standardization will help reduce complexity, improve interoperability, and ensure that AI systems can easily exchange information, enhancing their overall functionality and impact across industries.
3.Empower Two-Way Interaction
MCP protocol supports bidirectional communication, allowing AI models to both receive information and trigger actions in external systems. This capability transforms AI from a passive tool into an active participant in a broader ecosystem, enabling it to influence and interact with other systems in real time.
As a result, AI can respond dynamically to external events, initiate tasks, and make adjustments based on updated data, rather than simply reacting to input.
This bidirectional interaction significantly enhances the potential for more complex, interactive, and adaptive AI applications, enabling use cases such as real-time decision-making, automated workflows, and continuous system optimization.
4.Simplifying Tool Integration with a Common Language
MCP offering a structured, self-describing interface for tools. This allows each tool to define its capabilities in a standardized format, making it easier for the AI to understand and access them.
With MCP, the AI can invoke these capabilities using simple, natural-language commands instead of needing to know the specifics of each tool's API or data format. In essence, MCP enables all tools to communicate in a common language, reducing the need for complex, tool-specific knowledge. This streamlines the process and ensures that the AI can interact with a wide range of tools effortlessly.
5.Ensuring Data Security and Privacy with MCP
MCP incorporates advanced security features specifically designed to protect sensitive data, ensuring that all interactions between AI models and external systems are secure.
It provides robust mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access to critical resources, safeguarding both the integrity and confidentiality of the data being used.
This is essential for maintaining trust in AI systems, as sensitive information—whether personal, financial, or proprietary—must be handled with the utmost care.
By enforcing strict access controls, encryption protocols, and secure communication channels, MCP helps mitigate risks associated with data breaches, unauthorized manipulations, and other security threats, thereby ensuring the privacy and safety of the information AI models rely on.
How does MCP work?
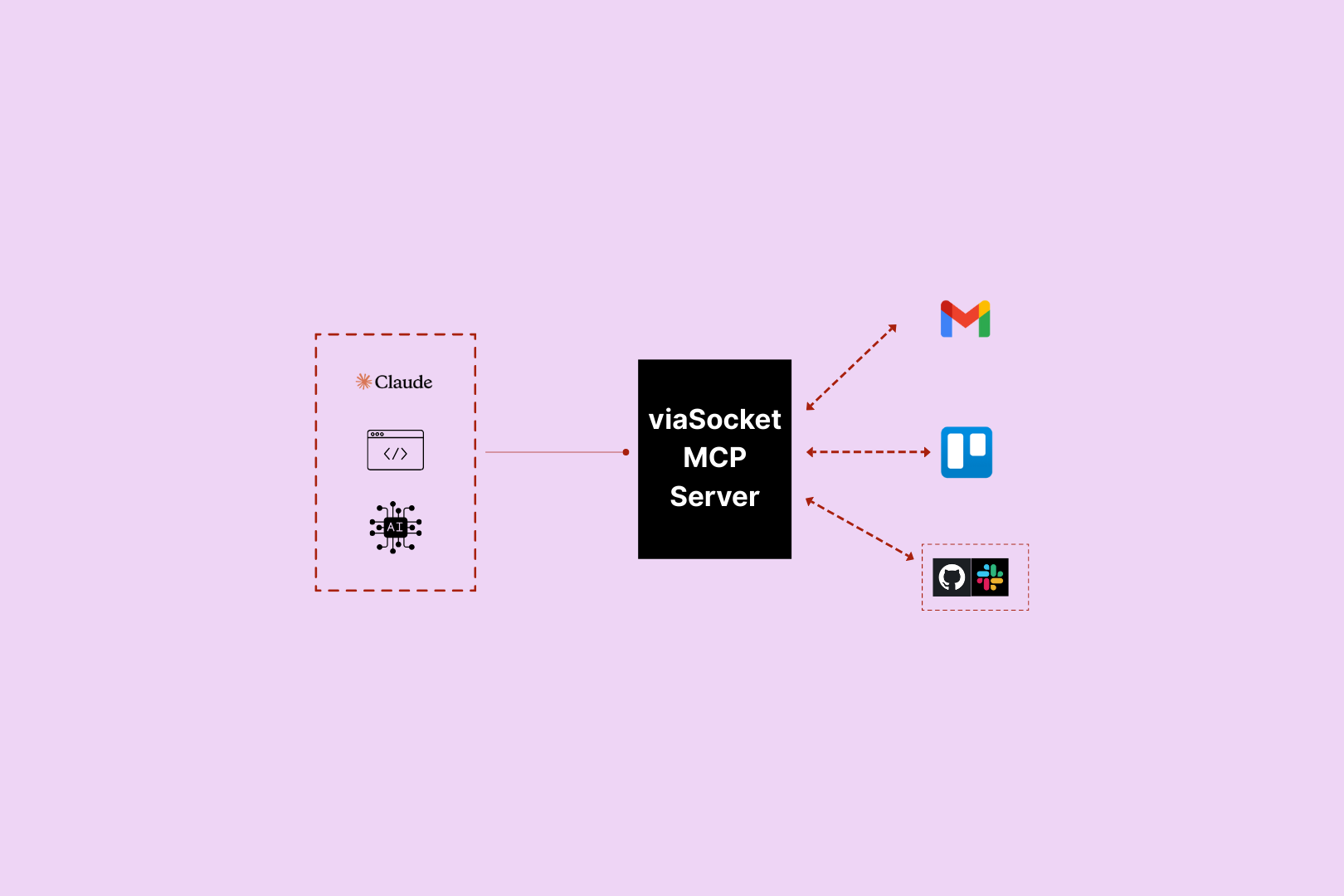
In MCP, there are three main roles that work together to make everything run smoothly: MCP Server, MCP Client, and MCP Host. Here's a simple breakdown of each role and how they work together:
1.MCP Server:
- The MCP Server is like a service that provides tools or data for the AI. It could give the AI access to things like documents, databases, or even weather information.
- Think of it as the "data provider" that offers resources the AI needs to do its job. These servers advertise their abilities, so the AI knows exactly what each server can do.
2.MCP Client:
- The MCP Client is the part that’s embedded within the AI model itself, like a large language model (LLM). It is responsible for communicating with the MCP Server.
- Whenever the AI needs to retrieve data or trigger an action, the MCP Client sends a request to the MCP Server and receives the response.
- Essentially, the MCP Client acts as the "messenger" that helps the AI interact with the MCP Servers to get the data or perform tasks.
3.MCP Host:
- The MCP Host is an application or platform that integrates both the LLM (AI model) and the MCP Client. For example, applications like Claude Desktop, Cursor, or other AI-powered assistants are MCP Hosts.
- The Host is where the AI lives and works. It brings together the LLM (AI model) and the MCP Client to make everything function smoothly, enabling the AI to access external resources or tools through the MCP Servers.
Real-World Examples of MCP Servers in Action
MCP servers are already being used in many real-world situations to make AI smarter and more useful. Here are a few examples of how they're being applied:
1. Data Management and Team Collaboration: Companies are using MCP servers to connect AI assistants with their internal tools. For example, AI can retrieve files from Google Drive, summarize Slack messages, or access project details from Confluence and Jira, helping teams work faster and smarter.
2.Customer Support: MCP servers are being used to help AI assist in customer service. For example, an AI connected to a CRM system like Salesforce can pull up customer details, track service tickets, or even update records. This allows AI to provide personalized and up-to-date customer support without needing to manually check multiple systems.
3.Software Development and DevOps: Developers are using MCP servers to help AI assist with coding tasks. For example, an AI can fetch code from GitHub or manage version control tasks like creating branches or drafting commit messages. AI can also perform web browser actions for testing or data scraping using tools like Puppeteer.
4.Research and Knowledge Discovery: In research, MCP servers help AI access large databases like arXiv for academic papers. This allows researchers to ask their AI assistant to find the latest research on specific topics. AI can also perform real-time web searches using servers like Brave Search or Google News to get the most up-to-date information.
5.Data Analytics and Monitoring: AI is being integrated with analytics tools. For instance, an AI can use an MCP server to run queries on live data from Postgres databases or fetch error reports from tools like Sentry. This makes AI a smart assistant that can analyze real-time data, helping developers fix issues quickly.
These examples are just the beginning. The MCP ecosystem is expanding rapidly as developers release new servers for various platforms. The great thing is that every new MCP server can be used by any MCP-enabled AI, creating a collaborative growth that benefits everyone. This is why many believe MCP servers are not just a passing trend, but a fundamental change in how we create AI-powered applications.
Current Status of MCP Servers
MCP (Model Context Protocol) was released as an open standard by Anthropic in November 2024.
Initially, the reaction was slow, but in the last few months, it has gained significant traction. In late March, even OpenAI, Anthropic’s main competitor, adopted it.
Applications Supporting MCP Integrations
| Application Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Claude Desktop App | Offers comprehensive MCP support, including resources, prompts, and tool integrations. |
| Claude Code | Integrates MCP for prompts and tools, enhancing coding efficiency. |
| 5ire | An open-source AI assistant supporting MCP tools, facilitating enhanced AI interactions. |
| BeeAI Framework | Incorporates MCP tools into agentic workflows, supporting advanced AI functionalities. |
| Cline | Utilizes MCP for tools and resources, enhancing coding capabilities within VS Code. |
| Continue | An open-source AI assistant with full MCP support, integrating resources, prompts, and tools. |
| Cursor | Supports MCP tools within its AI code editor, enhancing coding workflows. |
| Emacs MCP | Integrates MCP tools within Emacs, enhancing AI capabilities. |
| fast-agent | A Python framework supporting MCP tools, resources, and prompts for advanced AI workflows. |
| Genkit | Integrates MCP servers as clients or creates MCP servers from Genkit tools and prompts. |
| Goose | Enhances software development by automating coding tasks through MCP tools. |
| LibreChat | An open-source AI chat UI supporting multiple AI providers, including MCP integration. |
| mcp-agent | A framework for building agents using MCP, supporting tools, server management, and agent workflows. |
| Microsoft Copilot Studio | A SaaS platform supporting MCP tools for building custom AI applications. |
| Roo Code | Enables AI coding assistance via MCP, supporting tools and resources. |
| Sourcegraph Cody | An AI coding assistant implementing MCP through OpenCTX, supporting resources. |
| Superinterface | AI infrastructure supporting MCP tools, enhancing in-app AI assistants. |
| TheiaAI/TheiaIDE | Integrates MCP tools for agents within Theia AI and Theia IDE. |
| Zed | A high-performance code editor with MCP support, focusing on prompt templates and tool integration. |
Welcome to the Age of AI That Connects to Everything
MCP servers are changing the way AI works by connecting isolated AI models to the outside world. These servers act as bridges, allowing AI to interact with live data and perform useful tasks.
Instead of AI being limited to a static system, MCP servers enable it to be context-aware and responsive to real-time inputs. This makes AI smarter and more practical, as it can now use external tools like Slack or research papers, making the technology more connected and capable.
While the use of MCP servers is still in its early stages, it’s expanding quickly. Both big companies and open-source communities are working together to grow the ecosystem.
If you understand MCP servers now, you're ahead of the curve in the future of AI. This new standard allows AI to seamlessly fit into our digital world, whether you're using AI or building new integrations yourself. The era of truly connected AI has arrived, making the technology smarter, more accessible, and ready for a wide range of applications. 🚀
Connect Your LLMs with Thousands of Apps in just 3 Simple Steps